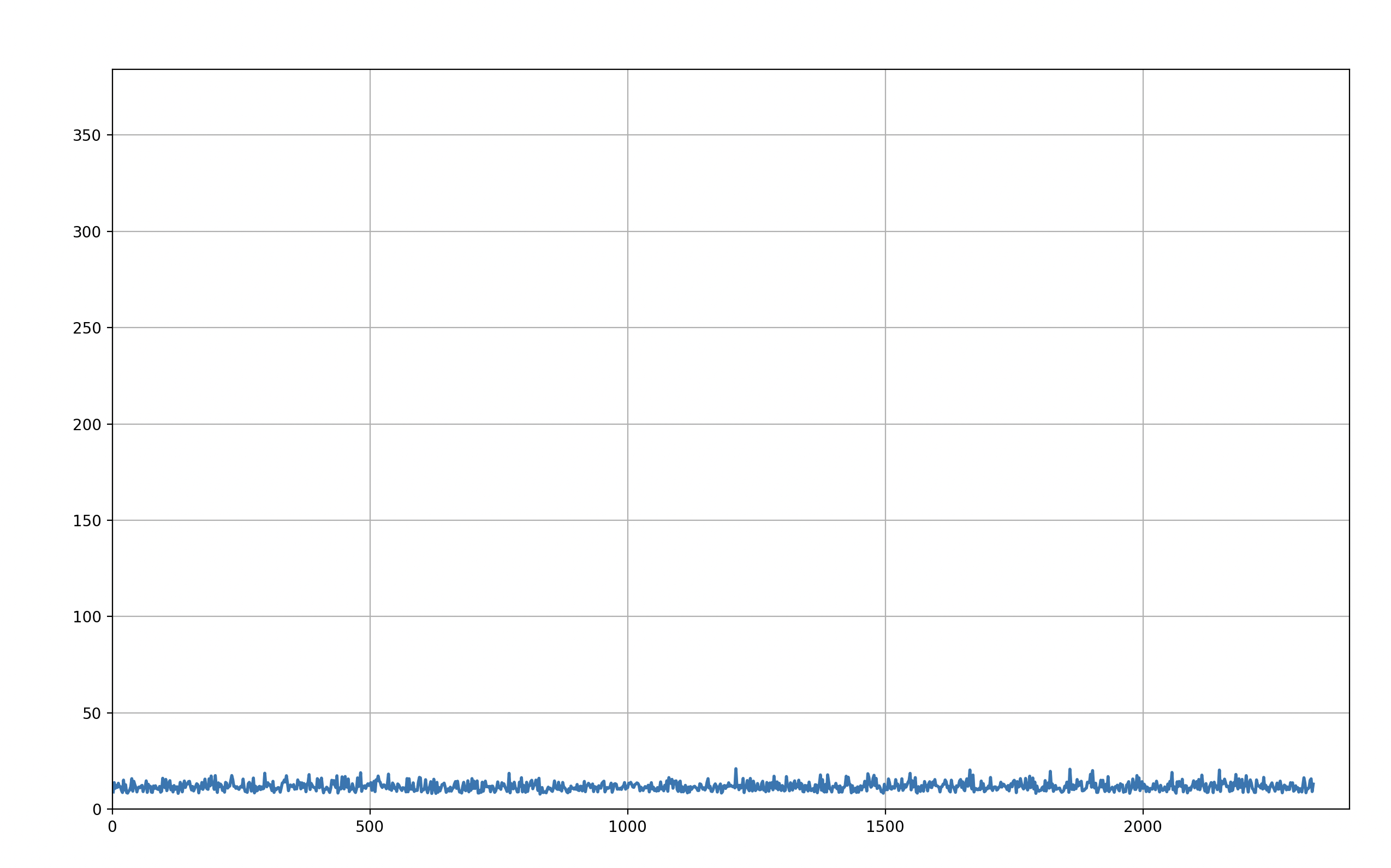
Here is a handy script that I often use to check the quality of the Zoom connection. It measures TCP latency instead of the usual ICMP stuff (which is often blocked).
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
TCP Ping Test (defaults to port 80, 10000 packets)
Usage: ./tcpping.py host [port] [maxCount]
- Ctrl-C Exits with Results
"""
"""
pip3 install matplotlib numpy
python3 ./tcp_ping_grapher.py 115.114.56.202 443 100
"""
import sys
import socket
import time
import signal
from timeit import default_timer as timer
# https://matplotlib.org/examples/animation/animate_decay.html
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
host = None
port = 80
# Default to 10000 connections max
maxCount = 10000
## Inputs
# Required Host
try:
host = sys.argv[1]
# host = "115.114.56.202"
except IndexError:
print("Usage: tcpping.py host [port] [maxCount]")
sys.exit(1)
# Optional Port
try:
port = int(sys.argv[2])
# port = 443
except ValueError:
print("Error: Port Must be Integer:", sys.argv[2])
sys.exit(1)
except IndexError:
pass
# Optional maxCount
try:
maxCount = int(sys.argv[3])
except ValueError:
print("Error: Max Count Value Must be Integer", sys.argv[3])
sys.exit(1)
except IndexError:
pass
# Pass/Fail counters
passed = 0
failed = 0
def getResults():
""" Summarize Results """
lRate = 0
if failed != 0:
lRate = failed / (count) * 100
lRate = "%.2f" % lRate
print("\nTCP Ping Results: Connections (Total/Pass/Fail): [{:}/{:}/{:}] (Failed: {:}%)".format((count), passed, failed, str(lRate)))
def signal_handler(signal, frame):
""" Catch Ctrl-C and Exit """
getResults()
sys.exit(0)
# Register SIGINT Handler
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
def work(t=0):
passed = 0
failed = 0
count = 0
maxCount = 3200
# Loop while less than max count or until Ctrl-C caught
while count < maxCount:
# Increment Counter
count += 1
success = False
# New Socket
s = socket.socket(
socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 1sec Timeout
s.settimeout(1)
# Start a timer
s_start = timer()
# Try to Connect
try:
s.connect((host, int(port)))
s.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RD)
success = True
# Connection Timed Out
except socket.timeout:
print("Connection timed out!")
failed += 1
except OSError as e:
print("OS Error:", e)
failed += 1
# Stop Timer
s_stop = timer()
s_runtime = "%.2f" % (1000 * (s_stop - s_start))
if success:
print("Connected to %s[%s]: tcp_seq=%s time=%s ms" % (host, port, (count-1), s_runtime))
passed += 1
# Sleep for 1sec
if count < maxCount:
# time.sleep(0.5)
# time.sleep(1)
time.sleep(2)
t += 2
yield t, float(s_runtime)
# Output Results if maxCount reached
# getResults()
def data_gen(t=0):
cnt = 0
while cnt < 1000:
cnt += 1
t += 0.1
yield t, np.sin(2*np.pi*t) * np.exp(-t/10.)
def init():
ax.set_ylim(0, 128 * 3)
ax.set_xlim(0, 300)
del xdata[:]
del ydata[:]
line.set_data(xdata, ydata)
return line,
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=2)
ax.grid()
xdata, ydata = [], []
def run(data):
# update the data
t, y = data
xdata.append(t)
ydata.append(y)
xmin, xmax = ax.get_xlim()
if t >= xmax:
ax.set_xlim(xmin, 2*xmax)
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
line.set_data(xdata, ydata)
return line,
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, run, work, blit=False, interval=10,
repeat=False, init_func=init)
plt.show()
Usage:
% python3 ./tcp_ping_grapher.py 115.114.56.202 443 100
Connected to 115.114.56.202[443]: tcp_seq=0 time=10.68 ms
Connected to 115.114.56.202[443]: tcp_seq=1 time=12.02 ms
Connected to 115.114.56.202[443]: tcp_seq=2 time=13.15 ms
Connected to 115.114.56.202[443]: tcp_seq=3 time=10.71 ms
...
Here is how the latency graph looks like: